Understanding what Steller sea lions and other pinnipeds consume is critical to understanding their sources of mercury intake.
There are many ways to assess what an animals eats, with pros & cons to each, and some being far more feasible for marine mammals that live in remote coastal areas.
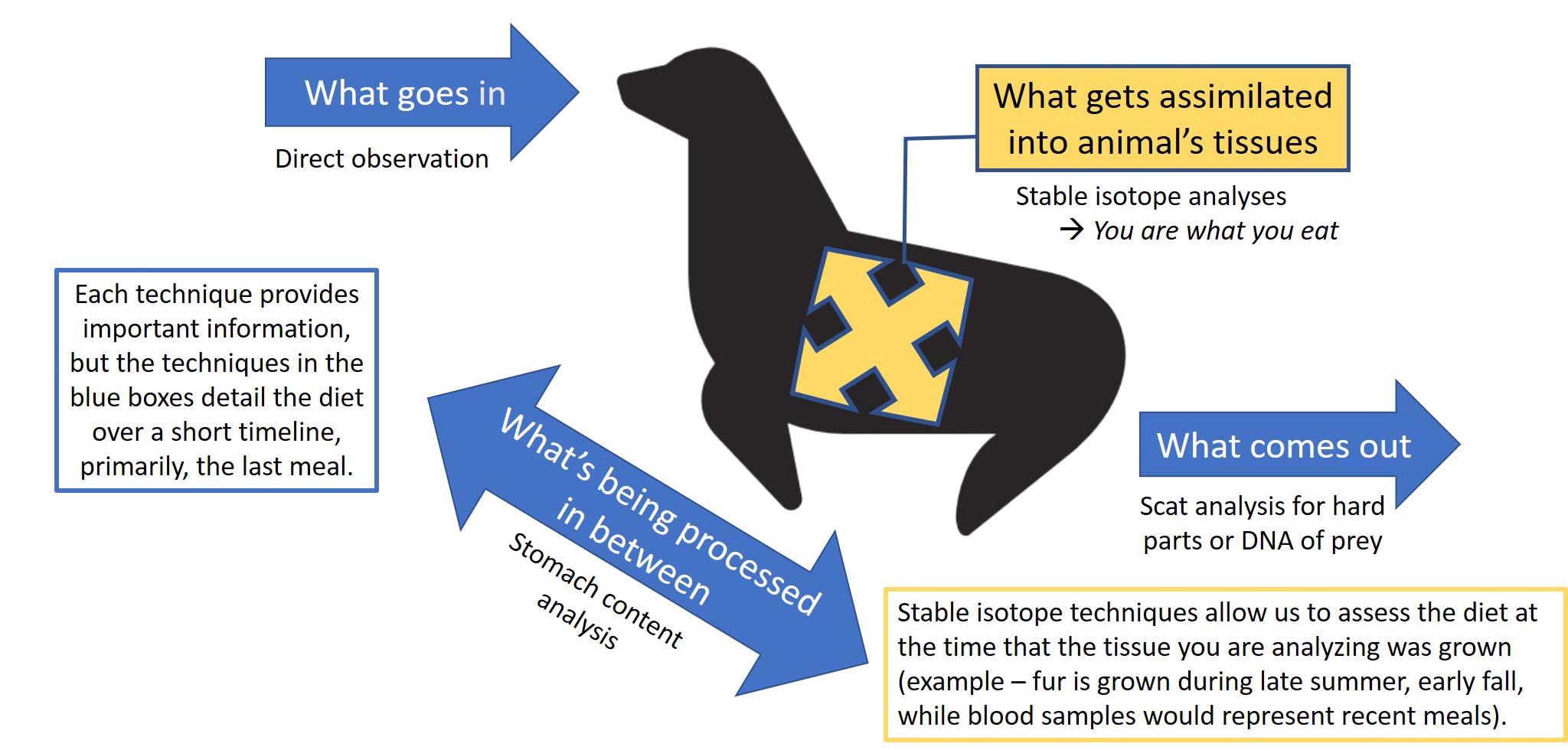
Laying out the relationships of who eats whom within an environment is the process of diagramming a food web. During the consumption of other organisms, nutrients, as well as any conntaminants in the organism are transferred to the consumer.

Mercury content in the muscle of fish
We partnered with Ocean Peace, Inc. to investigate the mercury content in the muscle of fish captured in the Aleutians.
In this study of 1052 individual fish, representing 19 different species, we found that


From top left to bottom right: Walleye Pollock, Pacific Cod, Pacific Ocean Perch, Arrowtooth Flounder, Kamchatka Flounder, Rock Sole, Yellow Irish Lord, Darkfin Sculpin, Atka Mackerel, Northern Rockfish, Pacific Octopus, Armhook Squid
Sampling hundreds of fish each day for several days at FISH-A-THON can make you a little crazy. Despite the long days, there were nothing but smiles from PIs, research professionals, and graduate students who all joined in the fun. Collectively we have now sampled over 1600 fish.

PIs Lorrie Rea (left) and Ben Barst (right) verified that we collected all the desired samples and logged them on datasheets.

Angie Gastaldi (second from left) teaches a Veterinary Student Scholar to sample Pacific octopus. Stephanie Crawford (center) proudly displays her fascination with cephalopods; and Maggie Castellini (right) ensures quality control of samples.
Former METAL graduate students Andrew Cyr, Michelle Trifari, Marianne Lian, and Mary Keenan got lots of hands-on fish-sampling experience during their years with METAL.
Results from the first few years of fish sampling are summarized in:
Cyr A, Lopez JA, Rea L, Wooller MJ, Loomis T, McDermott S, O’Hara TM (2019) Mercury concentrations in marine species from the Aleutian Islands: Spatial and biological determinants. Science of the Total Environment 664:761–770.
Fish compound specific stable isotopes
Trifari MP, Wooller MJ, Rea L, O'Hara TM, Lescord GL, Parnell AC, Barst BD (2024) Compound-specific stable isotopes of amino acids reveal influences of trophic level and primary production sources on mercury concentrations in fishes from the Aleutian Islands, Alaska. Science of The Total Environment 15:908:168242.
Stable isotopes in sea lion whiskers to inform about diet
Doll AC, Taras BD, Stricker CA, Rea LD, O’Hara TM, Cyr AP, Mcdermott S, Loomis TM, Wunder MB (2018) Temporal records of diet diversity dynamics in individual adult female Steller sea lion (Eumetopias jubatus) vibrissae. Oecologia 188:263-75.
Stricker CA, Christ AM, Wunder MB, Doll AC, Farley SD, Rea LD, Rosen DAS, Scherer RD, Tollit DJ (2015) Carbon and nitrogen isotope discrimination for Steller sea lion (Eumetopias jubatus) vibrissae relative to milk and fish/invertebrate diets. Marine Ecology Progress Series 523:255-266
Mercury in fish
Barst BD, Chételat J, Basu N (2022) Toxicological risk of mercury for fish and invertebrate prey in the Arctic. Science of The Total Environment 836:155702.
Barst BD, Dietz R, Basu N, Chételat J, Eulaers I, Wilson S (2022) What are the toxicological effects of mercury in Arctic biota? Part 3: Fish and invertebrates. Science of The Total Environment 836:155702.
Barst BD, Rosabal M, Drevnick PE, Campbell PG, Basu N (2018) Subcellular partitioning of trace elements (Cd, Pb, As, Hg, Se) in the livers of Alaskan yelloweye rockfish (Sebastes ruberrimus). Environmental Pollution 242:63-72.